Совместимость типов личности Майерса-Бриггса: какие люди предназначены друг для друга

Есть много способов понять, кто ты на самом деле и с какими людьми тебе будет наиболее комфортно общаться. Одни доверяют гороскопам и совместимости знаков зодиака, другие полагаются на соционику, третьи доверяют исключительно психологии. Любой из способов может быть рабочим, если не воспринимать его как единственную правду: истина всегда посередине.
Среди разных типологий в последнее время набирают популярность «персонажи» по Майерс-Бриггс. Эту типологию разработали писательница Изабель Бриггс Майерс и ее мать Катерина Кукс Бригс на основе типологии Юнга. Типология получила особое распространение в 1940-х годах и стала популярным в США и Европе способом определить профессиональные и личные задатки человека.
В настоящее время тесты по этой типологии включают в программу многих колледжей, несмотря на то, что в академических кругах насторожено относятся к этой классификации. Психологи и психиатры принимают типологию с множеством оговорок и признают, что это скорее забавный способ узнать себя, нежели работающий принцип, по которому стоит жить.
Какие типы бывают
Подробнее о разных типах личности мы рассказывали в отдельной статье. Если кратко, все люди обладают четырьмя параметрами, на основе которых проводится разделение: интроверсия/экстраверсия, сенсорика/интуиция, мышление/чувства, решения/восприятие.
Четыре параметра умножить на 4 варианта — получается 16 разных вариаций. Чтобы сэкономить время, мы не будем расписывать особенности каждого — это все есть в интернете. Вот они все:
Отношения
Люди с типом личности ENTP очень непредсказуемы, и они часто ищут партнеров, которые дополняют эту черту. Идеальные отношения для них включают поиск чего-то нового, того что оба партнера могли бы испробовать вместе. Это означает, что партнеры ENTP-личностей должны иметь аналогичные приоритеты и интеллектуальный потенциал. ENTP сделают все возможное, чтобы расширить границы и традиции любых романтических отношений, даже на ранней стадии знакомства (они часто проверяют насколько непредубежденные и спонтанные их потенциальные партнеры). Непоколебимый энтузиазм ENTP очень полезен в отношениях, он укрепляет и углубляет их.
ENTP постоянно бросают вызов себе и окружающим, всегда в поиске новых идей и способов улучшить их миропонимание. Это проявляется и в их романтических отношениях. Даже когда они находятся в поисках партнера, они уже размышляют о том, как они смогут развиваться и расти вместе с этим человеком.
 Хотя такое упорное стремление к росту может стать накладным, оно значительно укрепляет отношения. ENTP личности будут продолжать пытаться удивить своих партнеров, находить все новые аспекты для улучшения, искать новые пути для общения с близкими им и т.д. Встречаться с ENTP или жить с ними никогда не бывает скучно. Некоторые типы личности могут через некоторое время устать от этого, но если этого не произойдет, пламя их отношений всегда будет ярко гореть.
Хотя такое упорное стремление к росту может стать накладным, оно значительно укрепляет отношения. ENTP личности будут продолжать пытаться удивить своих партнеров, находить все новые аспекты для улучшения, искать новые пути для общения с близкими им и т.д. Встречаться с ENTP или жить с ними никогда не бывает скучно. Некоторые типы личности могут через некоторое время устать от этого, но если этого не произойдет, пламя их отношений всегда будет ярко гореть.
Эта черта особенно заметна в интимных ситуациях. ENTP-личности удивительные и восторженные сексуальные партнеры, они стремятся пробовать что-то новое и развиваться в этой области. ENTP призывают своих партнеров экспериментировать, наслаждаться интимными ситуациями и не ограничивать себя ни в чем. Как только отношения продвигаются к этой стадии, особенности ENTP делают их очень притягательными партнерами. Тем не менее, люди с этим типом личности редко рассматривают близость в эмоциональном плане, они склонны воспринимать половые акты с физической, а не духовной точки зрения.
ENTP знают, как направить свой огромный энтузиазм и искреннее желание улучшить положение вещей в развитие и улучшение романтических отношений. Тем не менее, ENTP-личности должны не игнорировать чувства своего партнера, а также избегать чрезмерных погружений в новые, не романтические идеи или возможности. Хотя эта неподдельная восторженность, безусловно, может быть очень привлекательной, но бесконечный поток идей, изливающийся из сознания ENTP, в конечном итоге может довести до фрустрации даже самых терпеливых партнеров.
Предпочтительные партнеры: INTP и ENTJ типы, так как их предпочтения к I (Интроверсии) и J (Суждению) балансируют предпочтения к P (Восприятию) и Е (Экстраверсии) ENTP.
ENFJ Relationship Compatibility With ALL Types
The ENFJ personality type is probably one of the most romantic of all the sixteen types (more on that here). ENFJs are fond of the idea of love, and when they fall in love with someone, they fall profoundly.
They are willing to do what it takes to make the relationship work, and even the smallest relationship troubles may leave them devastated.
What some may find particularly difficult when dealing with the ENFJ is that ENFJs tend to idealize their relationships and their partners.
This ENFJ tendency may stress out some other types who feel like they can’t meet their high expectations.
What makes you the way you are? Take THIS TEST to discover your personality type.
If you aren’t sure about your personality type, you may want to take this test first.
It’s important to mention that you don’t have to avoid certain personality types just because you don’t have much in common.
Even two completely different people can make their relationship work if they learn about each other’s preferences and commit to being considerate and respectful of each other’s needs.
ENFJ and ENFJ Compatibility
Ah, who can understand you better than somebody of your own type! ENFJ and ENFJ relationship MUST be wonderful because both consider their relationship a priority, and both are willing to work to make it even better.
Energetic and productive ENFJ & ENFJ couples enjoy planning their future together, are supportive of each other, and feel particularly secure because they can trust each other.
On the negative side, they might have issues because both are quite stubborn and feel very strongly about things.
If their opinions clash, none of the two is willing to compromise.
To make things worse, both tend to avoid confrontation and leave things unsaid for the sake of “peace”.
Of course, this doesn’t feel good and may undermine their connection with each other.
ENFJ and INTJ Compatibility
ENFJs and INTJs connect in several ways:
Problems may arise due to their different priorities. ENFJ’s priority is his or her relationship.
INTJ, on the other hand, is the most independent personality type that is mostly concerned with their intellectual pursuits and career.
The INTJ may not give as much attention as the ENFJ requires, leaving their ENFJ partner bitter and disappointed.

ENFJ and ESTP Compatibility
Energetic and expressive ENFJs are exactly what ESTPs are looking for.
ESTPs see their partners as playmates — someone they can have fun with and avoid negativity as much as possible.
The ENFJ likes the ESTP’s outgoing style; they both enjoy socializing and are likely to have an active social life as a couple.
Moreover, the ENFJ values the ESTP’s spontaneity, adventurousness, and generosity.
The ESTP, on the other hand, appreciates the ENFJ’s warmth, authenticity, and kindness.
ESTPs are very enthusiastic, and high energy partners, and, therefore, ENFJs are perfect for them.
On the negative side, the ESTP tends to get bored quickly, and if the ENFJ fails to keep things interesting, the ESTP may choose to have an affair.
To make things worse, the ENFJ avoids honest discussions and often fails to communicate his or her needs to the ESTP.
Unfortunately, ESTPs aren’t the type that understands their partners’ deep feelings without it being spelled out to them.
ENFJ and ISTP Compatibility
These two don’t have much in common, but that’s precisely what makes them so attractive to each other.
ISTPs like optimistic people who don’t make life more complicated than it should be, and ENFJs may feel attracted to somewhat mysterious ISTPs.
If they bond over a hobby or interest, they will probably end up married very soon.
One important thing to keep in mind is that the two communicate very differently. ENFJs are very verbal and expressive about their feelings while ISTPs feel like their partners should “just know” they are loved.
ISTPs would rather show their feelings through actions, such as small gifts and physical affection.
Both the ENFJ and the ISTP never discuss their problems.
ENFJs avoid confrontation for the sake of the relationship while ISTPs never discuss how they feel about their relationships with anyone, including their partners.
This lack of communication may make the relationship less satisfying for both.
The good thing is that both don’t give up on their relationship easily.
The ISTP won’t dump his or her partner unless there are very serious reasons to do so. Similarly, the ENFJ won’t break up with someone who did nothing wrong.
ENFJ and ENTJ Compatibility
Both ENFJs and ENTJs are future-oriented.
They enjoy making plans, setting goals, and reaching them. While ENFJs focus is primarily on their relationship, ENTJs focus is on advancing their career or business.
The ENTJ needs a stable partner who can take care of their relationship and family, and the ENFJ suits this role very well.
The ENFJ, on the other hand, appreciates the ENTJ’s loyalty, strength, confidence, energy, and leadership abilities.
Of course, there is a negative side too: ENFJs tend to take everything personally, and ENTJs can be very straightforward when expressing their opinions.
What the ENTJ thinks is constructive criticism may sound very harsh to the ENFJ.
The ENTJ, on the other hand, might think that the ENFJ always overreacts to everything, which is very tiring and distracting to the ENTJ.
ENFJ and INFJ Compatibility
These two have a lot in common and understand each other very well.
Both types value good communication, loyalty, and self-expression. Both are sensitive, warm, and affectionate.
Their main difference is their introversion / extroversion, which implies that the ENFJ is much more friendly and energetic than the INFJ.
INFJs can benefit from being involved in more activities and meeting more people. However, ENFJs have to be careful not to exhaust their partners with too many social interactions and too many plans.
The ENFJ partner has to be patient and allow the INFJ plenty of time to recover, be alone, think things through.
Considering the ENFJ’s natural tendency to act quickly, waiting for the INFJ to make up his or her mind about something can be very frustrating.
The INFJ, on the other hand, may feel that they are constantly pressured into something and that the ENFJ is always too busy to really focus and listen to what they have to say.
ENFJ and INFP Compatibility
ENFJ and INFP are a great match because both are very relationship-focused.
Both are very warm people who value authenticity and don’t like to play games.
A lot is going on for these two, and we’ve already discussed that in detail here.
On the negative side, active and energetic ENFJs may sometimes be too much to handle for INFPs who need space and time for themselves.
ENFJs, on the other hand, may think that INFPs are somewhat lazy and may resent them for being left with a disproportional amount of responsibilities and household chores.
ENFJ and ENTP Compatibility
ENFJs and ENTPs are very much alike: They are both spontaneous, fun-loving, energetic, and outgoing.
However, being the most introverted extravert, the ENTP is more assertive and needs some time alone. The two are likely to have interesting discussions and be very supportive of each other’s pursuits.
Problems may arise because of their different preferences when it comes to planning. The ENTP wants to keep his or her options open, but the ENFJ wants to plan things in advance.
Besides, when it comes to relationships, ENTPs have commitment issues (more on that here) while ENFJs want to know where they stand.

ENFJ and ESTJ Compatibility
Finally, someone who can give the ENFJ a stable and secure relationship they are looking for!
ESTJs, on the other hand, are attracted to ENFJs’ warmth, optimism, and original way of thinking.
On the negative side, the imaginative ENFJ may begin to feel bored with his or her ESTJ partner who is very down to earth. ENFJs want someone more romantic, but ESTJs are naturally practical, logical and very businesslike.
ESTJs may have their doubts too: They may see their ENFJ partners as irrational and overly emotional.
It is especially true when it comes to decision making.
ESTJs make decisions after carefully analyzing all relevant data while ENFJs make decisions based on their feelings and personal values.
Needless to say, such differences may result in a lot of arguments between the two.
ENFJ and ISTJ Compatibility
The ISTJ is another good option for the ENFJ.
Even though the two are very different people, they make a good team because they are good planners and like to stay organized.
When it comes to relationships, ISTJs are very similar to ESTJs (see above).
On the negative side, there may be a lack of communication as the ISTJ partner doesn’t share his or her innermost thoughts and feelings.
It doesn’t feel good on the ENFJ end because ENFJs always want to connect on a deeper level by discussing their feelings and emotions with their partner.
ENFJ and ESFP Compatibility
Energetic and fun-loving ESFPs may seem like a great match, but let’s be realistic — ESFPs have commitment issues. Even when they commit, they tend to get bored and move in and out of relationships quickly.
Although the two may have a great time together at the beginning of the relationship, the ENFJ may begin to feel insecure later on.
ENFJs want stable and secure relationships where they can trust their partners, but ESFPs aren’t always ready to provide that.
ENFJ and ESFJ Compatibility
The ESFJ is another excellent option for the ENFJ.
ENFJ & ESFJ relationship can be rewarding because both are very loyal, caring, and relationship-focused.
ESFJs are friendly and talkative, so the two are likely to have lots of interesting conversations and active social life.
Another huge plus: ESFJs are very organized people and like their homes orderly and well maintained — this is very important for ENFJs.
Both the ENFJ and the ESFJ value harmony and are likely to work on their relationship.
Moreover, they are likely to stay committed even when things get tough. Marriage is extremely important to both and especially to the ESFJ.
ENFJ & ESFJ relationship is very stable and affectionate.
On the negative side, they may sometimes compete for airtime because both are incredibly talkative.
Another potential problem is their desire to avoid unpleasant conversations, which may leave some issues unresolved.
ENFJ and ENFP Compatibility
Although ENFPs are far from perfect partners, they are very compatible with ENFJs.
They have lots of things in common, and a relationship with an ENFP is never dull or boring.
However, there are essential differences between the two, which can make the ENFJ partner very unhappy:
ENFJ and ISFP Compatibility
When it comes to relationships, both the ENFJ and the ISFP have similar values.
They both want loyal partners who understand them and who they could have fun with.
With that in mind, the likelihood of them ending up together and getting married is very high.
ISFPs make very nurturing and supporting partners. They are also very romantic and are ready to give up on other important things for the sake of their relationships.
There is a negative side too: ISFPs are very spontaneous and like to go with the flow while ENFJs want to plan things and know exactly where they are going.
The ENFJ may attempt to control the ISFP or express his or her dissatisfaction with the way the ISFP lives, which of course isn’t something the ISFP is going to appreciate.
Also, the ESFJ needs lots of social stimulation, while the ISFP prefers quiet activities alone or with close friends.
ISFPs may find the ENFJs too intense, too bossy and controlling.
They may feel like they are continually pressing them into doing something they don’t want to do.
This ENFJ habit can be very off-putting to naturally considerate and respectful ISFPs.
ENFJ and ISFJ Compatibility
ISFJs derive pleasure from caring for others and are known for their high sense of duty. It’s not surprising that they will make great partners for any personality type, including ENFJs.
Although ISFJs and ENFJs have more differences than similarities, their core values are similar — they prioritize relationships, want to be useful and respectable.
Problems may arise due to their different needs when it comes to social stimulation.
Just like other introverted types, the ISFJ may find the ENFJ too loud and intense.
The ENFJ, on the other hand, may find the ISFJ a little boring: In addition to being introverted, ISFJs resist change and avoid trying new things.
They are also slow to make decisions because they need to think things over, which can be very frustrating ENFJs.
ENFJ and INTP Compatibility
ENFJs and INTPs don’t have much in common, but they both make loyal and committed partners.
The ENFJ is fascinated by the INTP’s independence and creativity while the INTP is attracted to the ENFJ’s warmth, energy, and optimism.
If the two end up married, the ENFJ partner has to be prepared to arrange common social rituals, such as attending other people’s weddings or courtesy visits. The INTP can’t be bothered with this type of activities.
INTP’s unwillingness to participate in social life is a huge problem for ENFJs who crave social experiences and enjoy meeting new people.
Besides, the INTP isn’t particularly talkative, and the ENFJ partner will constantly try to get them open up and share.
Unfortunately, the INTP doesn’t appreciate the ENFJ’s efforts and ends up feeling nagged.
To make things worse, the INTP is terrible at household chores and couldn’t care less about other people’s opinion about their housekeeping or the way they look, which doesn’t sit well with the ENFJ.
Once again, if you aren’t sure about your personality type, try taking this test.
Once again, if you aren’t sure about your personality type, try taking this test.
All posts on ENFJs can be found here.
16 Personalities main page here.
All relationship compatibility posts can be found here (regularly updated with new posts).

ad ONLINE THERAPY THAT TRULY WORKS:
Online CBT Platform to Help Deal with Relationship Problems, Anxiety, Depression, Addiction, and More. Includes professional follow-up by a CBT therapist. Click here to get started.
Интертипные отношения: обзор
Д, Лытов, 1 октября 2005 – 26 февраля 2007
1. Гипотеза Аугустинавичюте-Медведева
и сводная таблица интертипных отношений
Итак, сначала посмотрим на таблицу – а ниже прочитаем о том, как и откуда она возникла.
| Мой партнёр >> Я сам VVV | 1 квадра (альфа) | 2 квадра (бета) | 3 квадра (гамма) | 4 квадра (дельта) | ||||||||||||
| Иррац. диада | Рац. диада | Иррац. диада | Рац. диада | Рац. диада | Иррац. диада | Рац. диада | Иррац. диада | |||||||||
| ENTp | ISFp | ESFj | INTj | ESTp | INFp | ENFj | ISTj | ENTj | ISFj | ESFp | INTp | ESTj | INFj | ENFp | ISTp | |
| ENTp: Искатель | Т | Д | А | Зр | Де | М | З+ | Р+ | Кв | Кф | Сэ | П | пз | пр | Рд | Пд |
| ISFp: Посредник | Д | Т | Зр | А | М | Де | Р+ | З+ | Кф | Кв | П | Сэ | пр | пз | Пд | Рд |
| ESFj: Жизнелюб | А | Зр | Т | Д | пз | пр | Рд | Пд | Сэ | П | Кв | Кф | Де | M | З+ | Р+ |
| INTj: Аналитик | Зр | А | Д | Т | пр | пз | Пд | Рд | П | Сэ | Кф | Кв | M | Де | Р+ | З+ |
| ESTp: Маршал | Де | М | З+ | Р+ | Т | Д | А | Зр | пз | пр | Рд | Пд | Кв | Кф | Сэ | П |
| INFp: Лирик | М | Де | Р+ | З+ | Д | Т | Зр | А | пр | пз | Пд | Рд | Кф | Кв | П | Сэ |
| ENFj: Наставник | пз | пр | Рд | Пд | А | Зр | Т | Д | Де | М | З+ | Р+ | Сэ | П | Кв | Кф |
| ISTj: Инспектор | пр | пз | Пд | Рд | Зр | А | Д | Т | M | Де | Р+ | З+ | П | Сэ | Кф | Кв |
| ENTj: Предпринимат. | Кв | Кф | Сэ | П | З+ | Р+ | Де | М | Т | Д | А | Зр | Рд | Пд | пз | пр |
| ISFj: Хранитель | Кф | Кв | П | Сэ | Р+ | З+ | M | Де | Д | Т | Зр | А | Пд | Рд | пр | пз |
| ESFp: Политик | Сэ | П | Кв | Кф | Рд | Пд | пз | пр | А | Зр | Т | Д | З+ | Р+ | Де | M |
| INTp: Критик | П | Сэ | Кф | Кв | Пд | Рд | пр | пз | Зр | А | Д | Т | Р+ | З+ | M | Де |
| ESTj: Администратор | З+ | Р+ | Де | M | Кв | Кф | Сэ | П | Рд | Пд | пз | пр | Т | Д | А | Зр |
| INFj: Гуманист | Р+ | З+ | M | Де | Кф | Кв | П | Сэ | Пд | Рд | пр | пз | Д | Т | Зр | А |
| ENFp: Психолог | Рд | Пд | пз | пр | Сэ | П | Кв | Кф | З+ | Р+ | Де | M | А | Зр | Т | Д |
| ISTp: Мастер | Пд | Рд | пр | пз | П | Сэ | Кф | Кв | Р+ | З+ | M | Де | Зр | А | Д | Т |
Условные обозначения
Описания отношений можно прочесть, щёлкнув по соответствующим ссылкам. При этом нужно иметь в виду, что описания говорят только о тенденции, не надо воспринимать их слишком буквально.
Согласно подходу Аугустинавичюте-Медведева, комфортность-некомфортность отношений зависит от взаимодействия между функциями Моделей А соответствующих типов. Так, если программная (1-я) функция одного из типов приходится на болевую (4-ю) другого – это сигнал о потенциальном дискомфорте при долговременных и тесных отношениях.
В этой гипотезе есть один момент, который авторы почти не рассмотрели. Из описания функций Модели А напрямую следует не только то, что они имеют разную «силу», но также то, что они реагируют с разной скоростью и имеют разную чувствительность (или, если угодно, «разрешающую способность»). Отсюда следует не только различная комфортность отношений, но также то, что, во-первых, при равном психологическом расстоянии разные отношения будут с разной скоростью «созревать»; во-вторых, зная пределы перегрузки той или иной функции, психологическое расстояние можно регулировать, повышая или понижая комфортность отношений. Разумеется, если бы «силу» и т.п. соционических функций можно было измерить, это позволило бы делать прогнозы развития отношений. Увы, пока что соционические функции только описываются, но не измеряются – лишнее доказательство того, что соционика – пока ещё только гипотеза, но никак не «научное открытие».
Кроме того, в соционике почти не изучена проблема того, как накладываются друг на друга интертипные отношения при общении в группе; описаны, пока предварительно, лишь некоторые малые группы из 4 типов, где отношения образуют симметричную картину. Из этих групп традиционно наиболее комфортными считаются квадры, а наиболее близкими по способам реализации способностей – клубы.
Совершенно не изучена проблема воздействия на соционические функции людей «нечеловеческих» факторов; по этому вопросу в соционике нет ясных соображений, если не считать, на мой взгляд, ошибочные по сути гипотезы «типирования неодушевлённых объектов» и «аналогии между отношениями и типами».
Наконец, не изучена проблема возрастного развития отношений. Речь идёт не только о «приспособлении» и «притирании» потенциально конфликтных пар, или об угасании интереса друг к другу в комфортных парах, но и о том, что различные соционические функции, теоретически, могут в разном возрасте иметь разную силу. Данные психофизиологов (которые совсем не знакомы с соционикой) говорят, например, что в раннем детстве ещё не развиты функции суждения, что эмоциональность угасает с возрастом – разве это не должно сказываться на отношениях?
Добавлю, что лишь в последние годы появились описания отношений в каждой из возможных пар типов. Сначала появились описания каждой из дуальных пар (В.Мегедь и А.Овчаров), которые размещены на нашем сайте, затем Е.Филатова и независимо от неё П.Цыпин предложили описания всех возможных пар типов. При этом у Филатовой родилась гипотеза, не укладывающаяся в традиционные представления о соционических отношениях.
Альтернативные гипотезы
о системах интертипных отношений
на основе юнговской типологии
Альтернативные гипотезы, хотя они также привязаны к юнговским типам, тем не менее, представляют несколько иную картину отношений.
Подход 1-й: совпадение-расхождение двоичных признаков
Отношения строятся не на основе Модели А, а на основе совпадения-расхождения двоичных признаков типа (сенсорика-интуиция, логика-этика и т.д., а также гипотетических признаков Рейнина). Такую гипотезу предложил в 1985 г. Г. Рейнин (см. отношения Рейнина). Восемь из них совпадают с отношениями по системе Аугустинавичюте, остальные – отличаются. Асимметричные отношения при таком подходе, разумеется, отсутствуют. Стоит отметить, что отношения Рейнина существуют в соционике чисто формально и на практике, насколько мне известно, никем из социоников не используются.
Подход, аналогичный подходу Рейнина, положен в основу модели отношений, которую предложили американцы Джо Батт и Марина Маргарет Хэйс, сторонники типологии Майерс-Бриггс. Их гипотеза не признана большинством сторонников данной типологии; в то же время, предложенные ими описания типов и отношений довольно близки к соционическим.
Подход В.В.Гуленко является компромиссным между подходом Рейнина и подходом Аугустинавичюте-Медведева (см. таблицу ниже). Номера в таблице обозначают функции Вашей модели А, на которые попадают соответствующие сильные функции партнёра.
1 | 2 |
4 | 3 |
6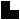 | 5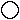 |
7 | 8 |
– СЛИ, Мастер
– ЛИЭ, Предприниматель
– СЭЭ, Политик
Подход 2-й: не функции, а блоки
Запоминание отношений по Модели А – довольно сложная процедура. Е. Шепетько решил усовершенствовать и упростить данный подход. Из Модели А видно, что функции расположены в ней не произвольно, а согласно чёткой закономерности; например, если в блоке Эго находится ЧЛ, то в блоке Суперид обязательно будет БЭ, в блоке Суперэго – ЧЭ, в блоке Ид – БЛ. Значит, все разновидности соционических отношений можно рассматривать на основе 4-х «простых свойств», т.е. «поблочно». При этом система отношений «смазывается», зато легче запоминается. Подход Шепетько развили и усовершенствовали С.А.Богомаз и В.В.Гуленко. Подробнее см. – Функциональный анализ отношений.
Подход 3-й: одни признаки «хуже», другие «лучше»,
но не вообще, а в зависимости от ситуации взаимодействия
Основан на том, что сами по себе признаки типов играют различную роль в восприятии партнёрами друг друга и их способности ужиться. В частности, отмечается, что отношения двух логиков – совсем не то же, что отношения двух этиков, и т.д. Такой подход впервые предложила Е. Филатова (2001). Кроме того, Филатова отмечала важную роль совпадения признаков типов с распространёнными в обществе поведенческими стереотипами и распределением ролей между полами. Согласно Филатовой, признаки сенсорика и этика коррелируют со стереотипом «сексуальность», сенсорика и логика – «мужественность», интуиция и этика – «женственность», и т.д. При таком подходе возрастает роль таких «несоционических» факторов, как пол и возраст. Так, согласно Филатовой, дуальная пара ИЛЭ (м) – СЭИ (ж) имеет более высокие шансы на совместимость, чем пара ИЛЭ (ж) – СЭИ (м). При этом Филатова не отрицает гипотезу об интертипных отношениях А. Аугустинавичюте.
Подход 4-й: хаотично-эмпирический:
Американец Александр Авила полагает, что для каждого типа существует своя, неповторимая система отношений, в которой нет никаких закономерностей – её можно только вывести эмпирически. Другие исследователи гипотезу Авилы не подтвердили.
Другие гипотезы (не на основе юнговских типов)
Существуют и другие гипотезы – см. статью Психологическая совместимость.