Html форма для ввода номера телефона
За установку цвета в HTML5 отвечает специальный элемент input с типом color :
Элемент отображает выбранный цвет. А при нажатии на него появляется специальное диалоговое окно для установки цвета:

Значением этого элемента будет числовой шестнадцатеричный код выбранного цвета.
С помощью элемента datalist мы можем задать набор цветов, из который пользователь может выбрать нужный:

Поля для ввода url, email, телефона
Для их настройки мы можем использовать те же атрибуты, что и для обычного текстового поля:
maxlength : максимально допустимое количество символов в поле
pattern : определяет шаблон, которому должен соответствовать вводимый текст
placeholder : устанавливает текст, который по умолчанию отображается в поле
readonly : делает текстовом поле доступным только для чтения
required : указывает, что текстовое поле обязательно должно иметь значение
size : устанавливает ширину поля в видимых символах
value : устанавливает значение по умолчанию для поля
list : устанавливает привязку к элементу datalist со списком возможных значений

Основное преимущество подобных полей ввода перед обычными текстовыми полями состоит в том, что поля ввода для email, url, телефона для проверки ввода используют соответствующий шаблон. Например, если мы введем в какое-либо поле некорректное значение и попробуем отправить форму, то браузер может отобразить нам сообщение о некорректном вводе, а форма не будет отправлена:
Html форма для ввода номера телефона
Despite the fact that inputs of type tel are functionally identical to standard text inputs, they do serve useful purposes; the most quickly apparent of these is that mobile browsers — especially on mobile phones — may opt to present a custom keypad optimized for entering phone numbers. Using a specific input type for telephone numbers also makes adding custom validation and handling of phone numbers more convenient.
Note: Browsers that don’t support type tel fall back to being a standard text (en-US) input.
Value
The element’s value attribute contains a DOMString that either represents a telephone number or is an empty string ( «» ).
Additional attributes
In addition to the attributes that operate on all elements regardless of their type, telephone number inputs support the following attributes:
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
| maxlength | The maximum length, in UTF-16 characters, to accept as a valid input |
| minlength | The minimum length that is considered valid for the field’s contents |
| pattern | A regular expression the entered value must match to pass constraint validation |
| placeholder | An example value to display inside the field when it has no value |
| readonly | A Boolean attribute which, if present, indicates that the field’s contents should not be user-editable |
| size | The number of characters wide the input field should be onscreen |
maxlength
The input will fail constraint validation if the length of the text entered into the field is greater than maxlength UTF-16 code units long.
minlength
The telephone number field will fail constraint validation if the length of the text entered into the field is fewer than minlength UTF-16 code units long.
pattern
See Pattern validation below for details and an example.
placeholder
The placeholder attribute is a string that provides a brief hint to the user as to what kind of information is expected in the field. It should be a word or short phrase that demonstrates the expected type of data, rather than an explanatory message. The text must not include carriage returns or line feeds.
If the control’s content has one directionality (LTR or RTL) but needs to present the placeholder in the opposite directionality, you can use Unicode bidirectional algorithm formatting characters to override directionality within the placeholder; see Overriding BiDi using Unicode control characters in The Unicode Bidirectional Text Algorithm for those characters.
Note: Avoid using the placeholder attribute if you can. It is not as semantically useful as other ways to explain your form, and can cause unexpected technical issues with your content. See Labels and placeholders in : The Input (Form Input) element for more information.
readonly
A Boolean attribute which, if present, means this field cannot be edited by the user. Its value can, however, still be changed by JavaScript code directly setting the HTMLInputElement value property.
Note: Because a read-only field cannot have a value, required does not have any effect on inputs with the readonly attribute also specified.
The size attribute is a numeric value indicating how many characters wide the input field should be. The value must be a number greater than zero, and the default value is 20. Since character widths vary, this may or may not be exact and should not be relied upon to be so; the resulting input may be narrower or wider than the specified number of characters, depending on the characters and the font ( font settings in use).
This does not set a limit on how many characters the user can enter into the field. It only specifies approximately how many can be seen at a time. To set an upper limit on the length of the input data, use the maxlength attribute.
Non-standard attributes
The following non-standard attributes are available to telephone number input fields. As a general rule, you should avoid using them unless it can’t be helped.
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
| autocorrect | Whether or not to allow autocorrect while editing this input field. Safari only. |
| mozactionhint | A string indicating the type of action that will be taken when the user presses the Enter or Return key while editing the field; this is used to determine an appropriate label for that key on a virtual keyboard. Firefox for Android only. |
Using tel inputs
Telephone numbers are a very commonly collected type of data on the web. When creating any kind of registration or e-commerce site, for example, you will likely need to ask the user for a telephone number, whether for business purposes or for emergency contact purposes. Given how commonly-entered phone numbers are, it’s unfortunate that a «one size fits all» solution for validating phone numbers is not practical.
Fortunately, you can consider the requirements of your own site and implement an appropriate level of validation yourself. See Validation, below, for details.
Custom keyboards
One of the main advantages of is that it causes mobile browsers to display a special keyboard for entering phone numbers. For example, here’s what the keypads look like on a couple of devices.
| Firefox for Android | WebKit iOS (Safari/Chrome/Firefox) |
|---|---|
 |  |
A simple tel input
In its most basic form, a tel input can be implemented like this:
Placeholders
Controlling the input size
You can control not only the physical length of the input box, but also the minimum and maximum lengths allowed for the input text itself.
Physical input element size
The physical size of the input box can be controlled using the size attribute. With it, you can specify the number of characters the input box can display at a time. In this example, for instance, the tel edit box is 20 characters wide:
Element value length
The size is separate from the length limitation on the entered telephone number. You can specify a minimum length, in characters, for the entered telephone number using the minlength attribute; similarly, use maxlength to set the maximum length of the entered telephone number.
The example below creates a 20-character wide telephone number entry box, requiring that the contents be no shorter than 9 characters and no longer than 14 characters.
Note: The above attributes do affect Validation — the above example’s inputs will count as invalid if the length of the value is less than 9 characters, or more than 14. Most browser won’t even let you enter a value over the max length.
Providing default options
As always, you can provide a default value for an tel input box by setting its value attribute:
Offering suggested values
With the element and its s in place, the browser will offer the specified values as potential values for the email address; this is typically presented as a popup or drop-down menu containing the suggestions. While the specific user experience may vary from one browser to another, typically clicking in the edit box presents a drop-down of the suggested email addresses. Then, as the user types, the list is adjusted to show only filtered matching values. Each typed character narrows down the list until the user makes a selection or types a custom value.
Here’s a screenshot of what that might look like:

Validation
As we’ve touched on before, it’s quite difficult to provide a one-size-fits-all client-side validation solution for phone numbers. So what can we do? Let’s consider some options.
Important: HTML form validation is not a substitute for server-side scripts that ensure the entered data is in the proper format before it is allowed into the database. It’s far too easy for someone to make adjustments to the HTML that allow them to bypass the validation, or to remove it entirely. It’s also possible for someone to simply bypass your HTML entirely and submit the data directly to your server. If your server-side code fails to validate the data it receives, disaster could strike when improperly-formatted data (or data which is too large, is of the wrong type, and so forth) is entered into your database.
Making telephone numbers required
You can make it so that an empty input is invalid and won’t be submitted to the server using the required attribute. For example, let’s use this HTML:
And let’s include the following CSS to highlight valid entries with a checkmark and invalid entries with a cross:
The output looks like this:
Pattern validation
If you want to further restrict entered numbers so they also have to conform to a specific pattern, you can use the pattern attribute, which takes as its value a regular expression that entered values have to match.
In this example we’ll use the same CSS as before, but our HTML is changed to look like this:
Notice how the entered value is reported as invalid unless the pattern xxx-xxx-xxxx is matched; for instance, 41-323-421 won’t be accepted. Neither will 800-MDN-ROCKS. However, 865-555-6502 will be accepted. This particular pattern is obviously only useful for certain locales — in a real application you’d probably have to vary the pattern used depending on the locale of the user.
Examples
In this example, we present a simple interface with a element that lets the user choose which country they’re in, and a set of elements to let them enter each part of their phone number; there is no reason why you can’t have multiple tel inputs.
Each input has a placeholder attribute to show a hint to sighted users about what to enter into it, a pattern to enforce a specific number of characters for the desired section, and an aria-label attribute to contain a hint to be read out to screenreader users about what to enter into it.
The example looks like this:
This is an interesting idea, which goes to show a potential solution to the problem of dealing with international phone numbers. You would have to extend the example of course to provide the correct pattern for potentially every country, which would be a lot of work, and there would still be no foolproof guarantee that the users would enter their numbers correctly.
It makes you wonder if it is worth going to all this trouble on the client-side, when you could just let the user enter their number in whatever format they wanted on the client-side and then validate and sanitize it on the server. But this choice is yours to make.
Как сделать маску телефона в форме HTML и Contact Form 7
Сегодня я расскажу вам, как можно улучшить форму обратной связи с помощью маски ввода телефона. Рассмотрим, как это реализовать на различных проектах.
Первый вариант – мы подключим маску к контактной форме на чистом html.
Второй вариант – мы рассмотрим, как сделать маску телефона для Contact Form 7, и заодно, как правильно подключать скрипты в WordPress через файл functions.php.
Сперва посмотрим о чем идет речь:
В это поле можно вводить только цифры, и строго то количество которое задано у вас в маске.
Итак начнем! В обоих случаях нужно скачать файлы плагина jQuery Masked Input по этой ссылке с официального репозитория. Также даю ссылку на документации по плагину на GitHub.
Маска ввода телефона к форме на html + js
1. Создаем простую форму
3. Подключаем скрипты плагина
После того как мы убедились, что библиотека JQuery подключена, распаковываем скаченный архив с плагином “jQuery Masked Input”. Внутри архива находим папку “dist” и забираем оттуда минимизированный файл “jquery.maskedinput.min.js”. Я обычно кладу этот файл в корень сайта в папку со всеми скриптами “js”, и подключаю его между тегами :
Далее нам нужно сделать вызов кода маски и привязать его к уникальному идентификатору. Мы можем сделать это прописав уникальный class или id к полю input. В нашем случае мы пропишем id phon. Далее просто перед формой нужно вставить вот этот код:
Или, чтобы не вставлять каждый раз код скрипта перед каждой формой, создаём отдельный файл js, например maskphone.js, туда вставляем код ниже и сохраняем в папку “js” в корне сайта.
4. Определяем в какой форме и в каком поле будет работать плагин.
Всё, что нам нужно сделать, чтобы идентифицировать поле, это указать class или id в нужном поле input. Пример на картинке. На практике используйте что-то одно.
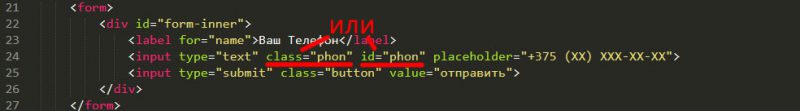
В примере, который я вам привёл, я использовал id – уникальное имя элемента. В таком случае, если у вас несколько одинаковых форм на одной странице маска телефона работать не будет. Так как id на странице может повторяться только 1 раз. Поэтому, если у вас на странице вызывается много раз одна и та же форма нужно прописать в поле input уникальный class.
А для активации скрипта в поле по class необходимо заменить код в maskphone.js на следующий:
С этим все, теперь рассмотрим как сделать тоже самое на одной из самых популярных CMS WordPress и дополнительного плагина к ней Contact Form 7.
Маска ввода для HTML элемента input

На этом уроке с помощью плагина masked input рассмотрим процесс создания различных масок ввода текстовым элементам формы.
Назначение плагина masked input
Плагин masked input предназначен для установления маски ввода элементу input с помощью кода JavaScript. Данный плагин для своего функционирования требует наличие подключённой библиотеки jQuery. Скачать плагин jquery.maskedinput.js ( jquery.maskedinput.min ) можно посредством следующей ссылки:
Подключение плагина
После того как Вы скачали этот плагин (файл js), его необходимо подключить. Это осуществляется с помощью элемента script :
Создание HTML маски ввода
Создания маски ввода осушествляется в js коде с помощью следующих знаков:
Создание HTML элементу input маски ввода телефона 
Если в качестве заполнителя Вы хотите использовать что-то другое, то его можно указать посредством параметра placeholder следующим образом:
Использование различных заполнителей в масках ввода masked input 
Например, выведем с помощью метода alert сообщение пользователю, когда он завершит ввод маски телефона:
Сообщение, отображаемое пользователю после того как он завершил ввод маски телефона 
Демонстрация работы маски для ввода числа с одним или двумя знаками после запятой 
Настройка маски ввода Masked Input
Например, создадим для маски специальный символ
Демонстрация работы маски для ввода положительного или отрицательного числа 
Например, создадим маску для ввода CSS цвета в шестнадцатеричном формате:
Демонстрация работы маски для ввода цвета CSS в шестандцатиричном формате 
Пример создания маски ввода телефона
Рассмотрим пример создания маски для ввода телефона в зависимости от выбранной страны:
Демонстрация работы маски для ввода телефона в зависимости от выбранной страны 
Html форма для ввода номера телефона
Despite the fact that inputs of type tel are functionally identical to standard text inputs, they do serve useful purposes; the most quickly apparent of these is that mobile browsers — especially on mobile phones — may opt to present a custom keypad optimized for entering phone numbers. Using a specific input type for telephone numbers also makes adding custom validation and handling of phone numbers more convenient.
Note: Browsers that don’t support type tel fall back to being a standard text input.
Value
The element’s value attribute contains a DOMString that either represents a telephone number or is an empty string ( «» ).
Additional attributes
In addition to the attributes that operate on all elements regardless of their type, telephone number inputs support the following attributes.
The values of the list attribute is the id of a element located in the same document. The provides a list of predefined values to suggest to the user for this input. Any values in the list that are not compatible with the type are not included in the suggested options. The values provided are suggestions, not requirements: users can select from this predefined list or provide a different value.
maxlength
The input will fail constraint validation if the length of the text entered into the field is greater than maxlength UTF-16 code units long.
minlength
The telephone number field will fail constraint validation if the length of the text entered into the field is fewer than minlength UTF-16 code units long.
pattern
The pattern attribute, when specified, is a regular expression that the input’s value must match in order for the value to pass constraint validation. It must be a valid JavaScript regular expression, as used by the RegExp type, and as documented in our guide on regular expressions; the ‘u’ flag is specified when compiling the regular expression, so that the pattern is treated as a sequence of Unicode code points, instead of as ASCII. No forward slashes should be specified around the pattern text.
If the specified pattern is not specified or is invalid, no regular expression is applied and this attribute is ignored completely.
Note: Use the title attribute to specify text that most browsers will display as a tooltip to explain what the requirements are to match the pattern. You should also include other explanatory text nearby.
See Pattern validation below for details and an example.
placeholder
The placeholder attribute is a string that provides a brief hint to the user as to what kind of information is expected in the field. It should be a word or short phrase that demonstrates the expected type of data, rather than an explanatory message. The text must not include carriage returns or line feeds.
If the control’s content has one directionality (LTR or RTL) but needs to present the placeholder in the opposite directionality, you can use Unicode bidirectional algorithm formatting characters to override directionality within the placeholder; see Overriding BiDi using Unicode control characters in The Unicode Bidirectional Text Algorithm for those characters.
Note: Avoid using the placeholder attribute if you can. It is not as semantically useful as other ways to explain your form, and can cause unexpected technical issues with your content. See Labels and placeholders in : The Input (Form Input) element for more information.
readonly
A Boolean attribute which, if present, means this field cannot be edited by the user. Its value can, however, still be changed by JavaScript code directly setting the HTMLInputElement value property.
Note: Because a read-only field cannot have a value, required does not have any effect on inputs with the readonly attribute also specified.
The size attribute is a numeric value indicating how many characters wide the input field should be. The value must be a number greater than zero, and the default value is 20. Since character widths vary, this may or may not be exact and should not be relied upon to be so; the resulting input may be narrower or wider than the specified number of characters, depending on the characters and the font ( font settings in use).
This does not set a limit on how many characters the user can enter into the field. It only specifies approximately how many can be seen at a time. To set an upper limit on the length of the input data, use the maxlength attribute.
Non-standard attributes
The following non-standard attributes are available to telephone number input fields. As a general rule, you should avoid using them unless it can’t be helped.
autocorrect
A Safari extension, the autocorrect attribute is a string which indicates whether or not to activate automatic correction while the user is editing this field. Permitted values are:
Enable automatic correction of typos, as well as processing of text substitutions if any are configured.
Disable automatic correction and text substitutions.
mozactionhint
A Mozilla extension, supported by Firefox for Android, which provides a hint as to what sort of action will be taken if the user presses the Enter or Return key while editing the field. This information is used to decide what kind of label to use on the Enter key on the virtual keyboard.
Using tel inputs
Telephone numbers are a very commonly collected type of data on the web. When creating any kind of registration or e-commerce site, for example, you will likely need to ask the user for a telephone number, whether for business purposes or for emergency contact purposes. Given how commonly-entered phone numbers are, it’s unfortunate that a «one size fits all» solution for validating phone numbers is not practical.
Fortunately, you can consider the requirements of your own site and implement an appropriate level of validation yourself. See Validation, below, for details.
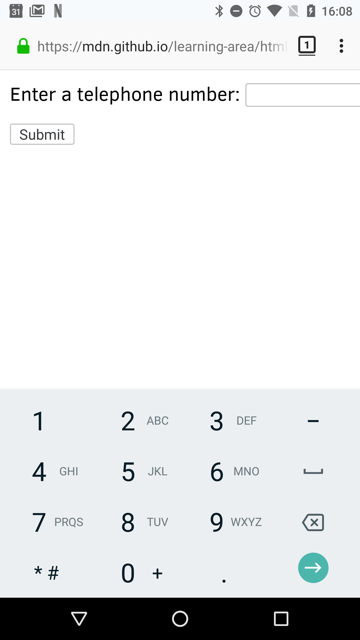
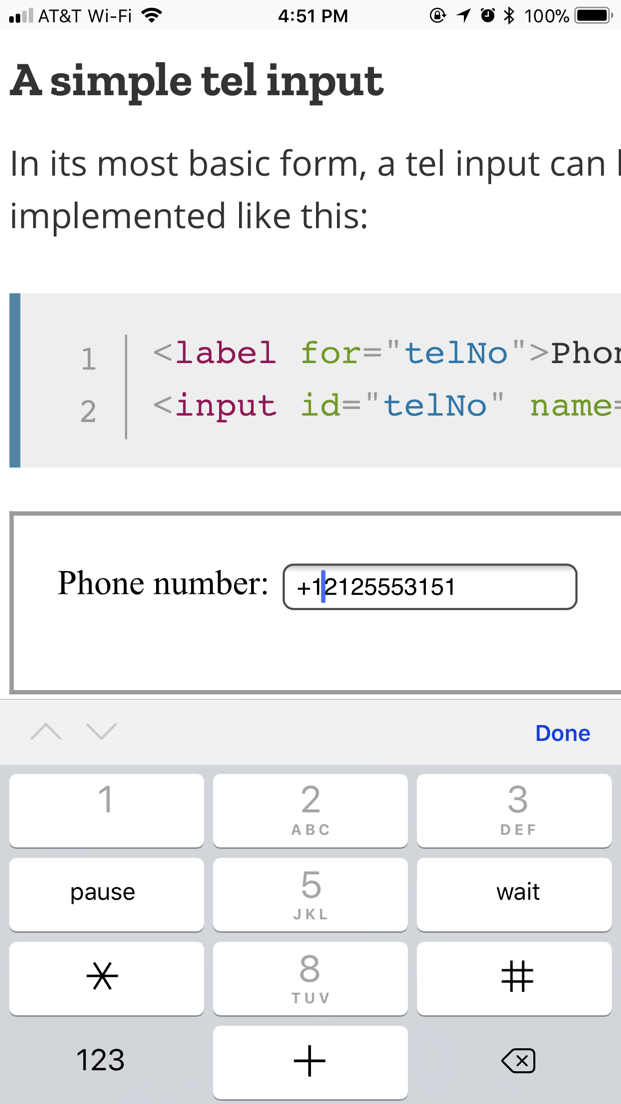
Custom keyboards
One of the main advantages of is that it causes mobile browsers to display a special keyboard for entering phone numbers. For example, here’s what the keypads look like on a couple of devices.
| Firefox for Android | WebKit iOS (Safari/Chrome/Firefox) |
|---|---|
 |  |
A simple tel input
In its most basic form, a tel input can be implemented like this:
Placeholders
Controlling the input size
You can control not only the physical length of the input box, but also the minimum and maximum lengths allowed for the input text itself.
Physical input element size
The physical size of the input box can be controlled using the size attribute. With it, you can specify the number of characters the input box can display at a time. In this example, for instance, the tel edit box is 20 characters wide:
Element value length
The size is separate from the length limitation on the entered telephone number. You can specify a minimum length, in characters, for the entered telephone number using the minlength attribute; similarly, use maxlength to set the maximum length of the entered telephone number.
The example below creates a 20-character wide telephone number entry box, requiring that the contents be no shorter than 9 characters and no longer than 14 characters.
Note: The above attributes do affect Validation — the above example’s inputs will count as invalid if the length of the value is less than 9 characters, or more than 14. Most browser won’t even let you enter a value over the max length.
Providing default options
Providing a single default using the value attribute
As always, you can provide a default value for an tel input box by setting its value attribute:
Offering suggested values
With the element and its s in place, the browser will offer the specified values as potential values for the email address; this is typically presented as a popup or drop-down menu containing the suggestions. While the specific user experience may vary from one browser to another, typically clicking in the edit box presents a drop-down of the suggested email addresses. Then, as the user types, the list is adjusted to show only filtered matching values. Each typed character narrows down the list until the user makes a selection or types a custom value.
Here’s a screenshot of what that might look like:
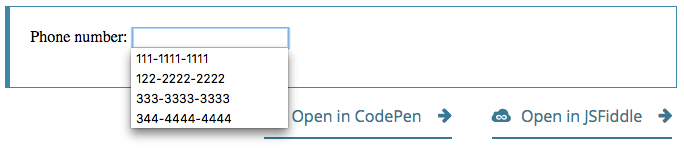
Validation
As we’ve touched on before, it’s quite difficult to provide a one-size-fits-all client-side validation solution for phone numbers. So what can we do? Let’s consider some options.
Warning: HTML form validation is not a substitute for server-side scripts that ensure the entered data is in the proper format before it is allowed into the database. It’s far too easy for someone to make adjustments to the HTML that allow them to bypass the validation, or to remove it entirely. It’s also possible for someone to bypass your HTML entirely and submit the data directly to your server. If your server-side code fails to validate the data it receives, disaster could strike when improperly-formatted data (or data which is too large, is of the wrong type, and so forth) is entered into your database.
Making telephone numbers required
You can make it so that an empty input is invalid and won’t be submitted to the server using the required attribute. For example, let’s use this HTML:
And let’s include the following CSS to highlight valid entries with a checkmark and invalid entries with a cross:
The output looks like this:
Pattern validation
If you want to further restrict entered numbers so they also have to conform to a specific pattern, you can use the pattern attribute, which takes as its value a regular expression that entered values have to match.
In this example we’ll use the same CSS as before, but our HTML is changed to look like this:
Notice how the entered value is reported as invalid unless the pattern xxx-xxx-xxxx is matched; for instance, 41-323-421 won’t be accepted. Neither will 800-MDN-ROCKS. However, 865-555-6502 will be accepted. This particular pattern is obviously only useful for certain locales — in a real application you’d probably have to vary the pattern used depending on the locale of the user.
Examples
In this example, we present a simple interface with a element that lets the user choose which country they’re in, and a set of elements to let them enter each part of their phone number; there is no reason why you can’t have multiple tel inputs.
Each input has a placeholder attribute to show a hint to sighted users about what to enter into it, a pattern to enforce a specific number of characters for the desired section, and an aria-label attribute to contain a hint to be read out to screenreader users about what to enter into it.
The example looks like this:
This is an interesting idea, which goes to show a potential solution to the problem of dealing with international phone numbers. You would have to extend the example of course to provide the correct pattern for potentially every country, which would be a lot of work, and there would still be no foolproof guarantee that the users would enter their numbers correctly.
It makes you wonder if it is worth going to all this trouble on the client-side, when you could just let the user enter their number in whatever format they wanted on the client-side and then validate and sanitize it on the server. But this choice is yours to make.